搜尋結果
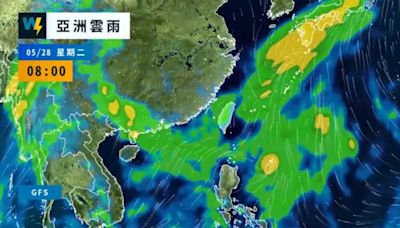
❗ 豪雨特報
鋒面接近,今(27)日南投、花蓮、高雄山區及屏東地區有局部大雨發生的機率,請注意瞬間大雨及強陣風,山區請慎防坍方及落石。
發布時間:05/27 18:41

哥倫布
OH, 美國
陰26°14°18°C- Monday雷雨26°14°
- Tuesday雷雨25°13°
- Wednesday零星陣雨20°11°
- Thursday晴朗22°11°
- Friday晴朗24°12°
Powered by
The climate in the United Kingdom is defined as a humid temperate oceanic climate, or Cfb on the Köppen climate classification system, a classification it shares with most of north-west Europe. [1] Regional climates are influenced by the Atlantic Ocean and latitude. Northern Ireland, Wales and western parts of England and Scotland, being ...
This article is about contemporary climate change. For historical climate trends, see Climate variability and change. Changes in surface air temperature over the past 50 years. [1] . The Arctic has warmed the most, and temperatures on land have generally increased more than sea surface temperatures.
- Composition
- Stratification
- Physical Properties
- Optical Properties
- Circulation
- Evolution of Earth's Atmosphere
- Images from Space
- See Also
- External Links
The three major constituents of Earth's atmosphere are nitrogen, oxygen, and argon. Water vapor accounts for roughly 0.25% of the atmosphere by mass. The concentration of water vapor (a greenhouse gas) varies significantly from around 10 ppm by mole fraction in the coldest portions of the atmosphere to as much as 5% by mole fraction in hot, humid a...
In general, air pressure and density decrease with altitude in the atmosphere. However, the temperature has a more complicated profile with altitude, and may remain relatively constant or even increase with altitude in some regions (see the temperature section, below). Because the general pattern of the temperature/altitude profile, or lapse rate, ...
Pressure and thickness
The average atmospheric pressure at sea level is defined by the International Standard Atmosphere as 101325 pascals (760.00 Torr; 14.6959 psi; 760.00 mmHg). This is sometimes referred to as a unit of standard atmospheres (atm). Total atmospheric mass is 5.1480×1018 kg (1.135×1019 lb), about 2.5% less than would be inferred from the average sea level pressure and Earth's area of 51007.2 megahectares, this portion being displaced by Earth's mountainous terrain. Atmospheric pressure is the total...
Temperature
The division of the atmosphere into layers mostly by reference to temperature is discussed above. Temperature decreases with altitude starting at sea level, but variations in this trend begin above 11 km, where the temperature stabilizes over a large vertical distance through the rest of the troposphere. In the stratosphere, starting above about 20 km, the temperature increases with height, due to heating within the ozone layer caused by the capture of significant ultraviolet radiation from t...
Density and mass
The density of air at sea level is about 1.2 kg/m3 (1.2 g/L, 0.0012 g/cm3). Density is not measured directly but is calculated from measurements of temperature, pressure and humidity using the equation of state for air (a form of the ideal gas law). Atmospheric density decreases as the altitude increases. This variation can be approximately modeled using the barometric formula. More sophisticated models are used to predict the orbital decay of satellites. The average mass of the atmosphere is...
Solar radiation (or sunlight) is the energy Earth receives from the Sun. Earth also emits radiation back into space, but at longer wavelengths that humans cannot see. Part of the incoming and emitted radiation is absorbed or reflected by the atmosphere. In May 2017, glints of light, seen as twinkling from an orbiting satellite a million miles away,...
Atmospheric circulation is the large-scale movement of air through the troposphere, and the means (with ocean circulation) by which heat is distributed around Earth. The large-scale structure of the atmospheric circulation varies from year to year, but the basic structure remains fairly constant because it is determined by Earth's rotation rate and...
Earliest atmosphere
The first atmosphere consisted of gases in the solar nebula, primarily hydrogen. There were probably simple hydrides such as those now found in the gas giants (Jupiter and Saturn), notably water vapor, methane and ammonia.
Second atmosphere
Outgassing from volcanism, supplemented by gases produced during the late heavy bombardment of Earth by huge asteroids, produced the next atmosphere, consisting largely of nitrogen plus carbon dioxide and inert gases.A major part of carbon-dioxide emissions dissolved in water and reacted with metals such as calcium and magnesium during weathering of crustal rocks to form carbonates that were deposited as sediments. Water-related sediments have been found that date from as early as 3.8 billion...
Third atmosphere
The constant re-arrangement of continents by plate tectonics influences the long-term evolution of the atmosphere by transferring carbon dioxide to and from large continental carbonate stores. Free oxygen did not exist in the atmosphere until about 2.4 billion years ago during the Great Oxygenation Event and its appearance is indicated by the end of the banded iron formations. Before this time, any oxygen produced by photosynthesis was consumed by the oxidation of reduced materials, notably i...
On October 19, 2015, NASA started a website containing daily images of the full sunlit side of Earth at https://epic.gsfc.nasa.gov/. The images are taken from the Deep Space Climate Observatory(DSCOVR) and show Earth as it rotates during a day.
Buchan, Alexander (1878). "Atmosphere" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. III (9th ed.). pp. 28–36.The National Weather Service ( NWS) is an agency of the United States federal government that is tasked with providing weather forecasts, warnings of hazardous weather, and other weather-related products to organizations and the public for the purposes of protection, safety, and general information.
In aviation, visual meteorological conditions ( VMC) is an aviation flight category in which visual flight rules (VFR) flight is permitted—that is, conditions in which pilots have sufficient visibility to fly the aircraft maintaining visual separation from terrain and other aircraft.
They are defined as lying in the most unusual ten percent (10th or 90th percentile of a probability density function). [2] The main types of extreme weather include heat waves, cold waves and heavy precipitation or storm events, such as tropical cyclones. The effects of extreme weather events are economic costs, loss of human lives, droughts ...
The Arctic oscillation ( AO) or Northern Annular Mode / Northern Hemisphere Annular Mode ( NAM) is a weather phenomenon at the Arctic pole north of 20 degrees latitude. It is an important mode of climate variability for the Northern Hemisphere. The southern hemisphere analogue is called the Antarctic oscillation or Southern Annular Mode (SAM).